Magnesium Benefits
Uses, Forms, and Side Effects ExplainedAre you getting enough magnesium? This essential mineral supports over 300 functions in your body, including nerve and muscle regulation, digestion, and hormone balance. Learn about the benefits of magnesium, different supplement forms, their effectiveness, and possible side effects.
Key Takeaways
-
Magnesium is essential for over 300 metabolic processes, supporting muscle function, digestion, hormone balance, and mental health.
-
Various forms of magnesium supplements, including oral and transdermal options, present both benefits and potential side effects, necessitating informed usage.
-
While transdermal magnesium shows promise for absorption through the skin, ongoing research is needed to confirm its effectiveness and safety.
The Importance of Magnesium in the Body
Magnesium is a silent hero in our bodies, quietly supporting over 300 metabolic processes that keep us functioning smoothly. It regulates nerve and muscle function, ensuring effective muscle contractions and overall physical performance. Additionally, magnesium supports healthy digestion, hormone balance, and calming the body, contributing significantly to our well-being.
A deficiency in magnesium can have serious repercussions. Symptoms like muscle weakness, fatigue, and headaches are often the first signs, but the long-term effects can be even more concerning. Low magnesium levels can disrupt muscle function, leading to cramps and abnormal muscle movements. Mental health is also affected, with deficiencies linked to increased risks of depression and anxiety.
Moreover, inadequate magnesium intake over time can elevate the risk of chronic health issues such as cardiovascular diseases and diabetes. Maintaining adequate magnesium levels is essential due to its extensive role in health. Optimal magnesium levels, whether achieved through diet or supplementation, can significantly enhance quality of life.
Forms of Magnesium Supplements
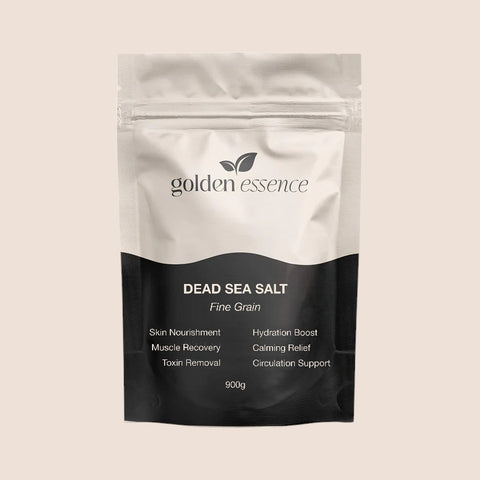
Several forms of supplementation can help boost magnesium levels. Oral magnesium supplementation is perhaps the most common, available in various forms like tablets, capsules, and powders. While effective in addressing magnesium deficiency, these supplements may cause gastrointestinal discomfort like diarrhea or cramping.
Transdermal magnesium, which includes products like magnesium chloride flakes, magnesium oil, magnesium cream, and magnesium flakes, offers an alternative that bypasses the digestive system. Magnesium chloride flakes, for instance, dissolve in water and are easily absorbed through the skin, providing relief for sore muscles, calming nerves, and improving sleep. Its ease of use and fewer side effects make transdermal magnesium appealing to many.
Skin thickness, hydration, and temperature influence the absorption rates of transdermal products. Although the skin’s outer layer acts as a barrier, hair follicles and sweat glands provide pathways for better absorption. Consequently, various products are tailored to enhance penetration and maximize benefits, making transdermal magnesium an effective supplement form.
Transdermal Magnesium: Myth or Reality?
The concept of transdermal magnesium is fascinating. Magnesium’s absorption through the skin, bypassing the gastrointestinal tract, provides a promising alternative to traditional oral supplements. Various forms of transdermal application, such as magnesium oil sprays, creams, and magnesium chloride solution, enhance skin penetration and absorption.
However, the effectiveness and safety of these methods are still under scrutiny. Some users report positive experiences, while others caution against potential skin irritation or allergic reactions from topical magnesium. Research is ongoing to validate the claims surrounding transdermal magnesium and establish its efficacy and safety.
Understanding the potential of transdermal magnesium requires delving deeper into its mechanisms and efficacy. This includes examining skin absorption mechanisms and reviewing current research on its effectiveness.
Understanding Transdermal Absorption
The skin primarily acts as a barrier, making significant transdermal absorption of magnesium ions challenging. Healthy skin is designed to protect the body from external substances, which includes limiting the penetration of magnesium. However, there are certain pathways that can facilitate absorption.
Magnesium ions penetrate more effectively through hair follicles and sweat glands, covering a minor portion of the skin’s surface. Magnesium chloride-based products demonstrate better absorption rates through these pathways. Grasping these mechanisms is crucial for developing effective transdermal magnesium products.
Effectiveness of Transdermal Magnesium
Research on the effectiveness of transdermal magnesium has yielded mixed results. A pilot study noted a significant increase in serum magnesium levels after using a transdermal magnesium cream, particularly in non-athletic individuals. However, the overall statistical significance was not strong enough to draw definitive conclusions.
Current research underscores the need for more robust studies to confirm the effectiveness of transdermal magnesium products. Although some findings are promising, the variability in results emphasizes the necessity of continued research to fully understand the benefits and limitations of this supplementation method.
Benefits of Magnesium for Muscle Health
Magnesium plays a crucial role in maintaining muscle health. It supports proper muscle function by regulating contractions, promoting relaxation, and easing tension. Adequate magnesium levels can alleviate muscle cramps and discomfort, especially in the legs and feet. This makes magnesium essential for athletes and active individuals.
Long-term magnesium deficiency can disrupt the transport of essential nutrients, leading to muscle cramps and abnormal heart rhythms. Magnesium supplementation can significantly relieve nighttime leg cramps, especially during pregnancy.
Magnesium sulfate, or Epsom salt, is often used in baths for muscle relaxation and pain relief. Ensuring adequate magnesium intake, through oral supplementation or transdermal application, is crucial for muscle health and overall physical well-being.
Magnesium for Stress and Sleep Disorders
In our hectic lives, stress and sleep disorders are common issues. Magnesium improves sleep quality and reduces daytime fatigue, making it valuable in combating these issues. Magnesium can alleviate insomnia symptoms and improve overall sleep patterns, particularly in older adults.
Magnesium Glycinate is recommended for its calming properties, aiding in relaxation and sleep. Magnesium L-Threonate enhances brain function, potentially improving cognitive abilities and supporting better sleep.
Magnesium Everyday Bath Salts relax and soothe muscle aches and tension, promoting better sleep and reducing stress. Using these bath salts 2-3 times a week offers physical and mental relaxation, making them a beneficial addition to your routine.
Safety and Side Effects of Magnesium Supplementation
While beneficial, magnesium supplementation has potential side effects to be aware of. Oral magnesium supplements can cause gastrointestinal issues like diarrhea, nausea, or cramping, especially at higher dosages. Excessive intake can lead to severe health issues, including irregular heartbeats and, in extreme cases, cardiac arrest.
Consulting a healthcare provider before starting magnesium supplementation is crucial, especially for those with kidney problems. A healthcare professional can determine the appropriate dosage and form of magnesium to avoid adverse effects.
Safety should always be a priority when incorporating new dietary supplements into your regimen.
Summary
Magnesium is an essential mineral that supports numerous bodily functions, from muscle health to stress reduction and improved sleep. While there are various forms of supplementation available, the potential of transdermal magnesium offers an intriguing alternative. Although more research is needed to confirm its effectiveness, the benefits of maintaining adequate magnesium levels are clear. Always consult a healthcare professional to determine the best approach for your individual needs, ensuring safe and effective use.